EB-5 Professionals & Investors
EB-5 Economics 101
Why is an economic analysis needed for EB-5 regional center projects?
A regional center-based investor must invest in a new commercial enterprise and create ten (10) jobs per EB-5 investor. To project the number of jobs created by the investment an economic impact analysis must be conducted to demonstrate the requisite job creation. Economic analyses are reviewed and approved by the USCIS and must clearly apply approved methodologies to the project-specific data.
The economic analysis can include direct and indirect jobs created by the investment. Direct jobs are actual identifiable jobs for qualified employees located within the commercial enterprise into which the EB-5 investor has directly invested his or her capital. Indirect jobs are those jobs shown to have been created collaterally or as a result of capital invested in a commercial enterprise affiliated with a regional center by an EB-5 investor.
How are economic analyses conducted for the EB-5 program?
To perform the economic analysis, an input/output model is typically used. RIMS II and IMPLAN are the two most popular models used for EB-5 studies although other models are acceptable as well. The RIMS II model is produced by the US Bureau of Economic Analysis under the US Department of Commerce. IMPLAN is an economic impact modeling system created and provided by MIG, Inc, a private company. Generally speaking, an input/output model is a quantitative economic model that represents the interdependencies between different industries in an economy. The relationships between industries are used to estimate the ripple effects of initial changes in economic activity and determine the total economic impact of an activity.
What are the major factors in determining the overall job creation and economic impact of an EB-5 project?
There are many factors that affect the overall job creation and economic impact. The input/output model will generate an industry and geographic specific economic impact multiplier to apply to some economic activity – output, employment or workers’ earnings. Here are some common factors that affect the size of the resulting impact.
Impact area geography – Larger geographical areas or more populated areas tend to result in larger multipliers and therefore greater overall job creation. The urge to expand the geographical area must be balanced against the ability to provide justification for the impact area. The impact area must align with the geographical areas from which major inputs are purchased and/or where employees reside.
NAICS Code – The NAICS code refers to the North American Industry Classification System code. Ultimately, the business activity will dictate the appropriate NAICS code classification.
Does the job creation depend only on the EB-5 investment or the total investment?
The economic analysis and job creation will reflect the activity generated by the entire project. Accordingly, if your planned project does not create enough jobs to create the minimum 10 jobs per investor, you may consider reducing the number of investors and increasing non-EB-5 funding to meet the job requirement. All else equal, reducing the number of EB-5 investors will not reduce allowable job creation.
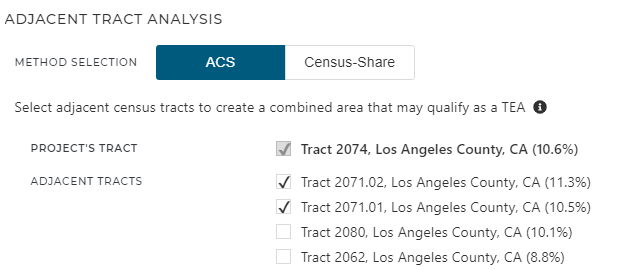
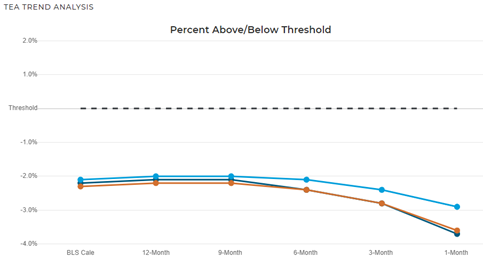
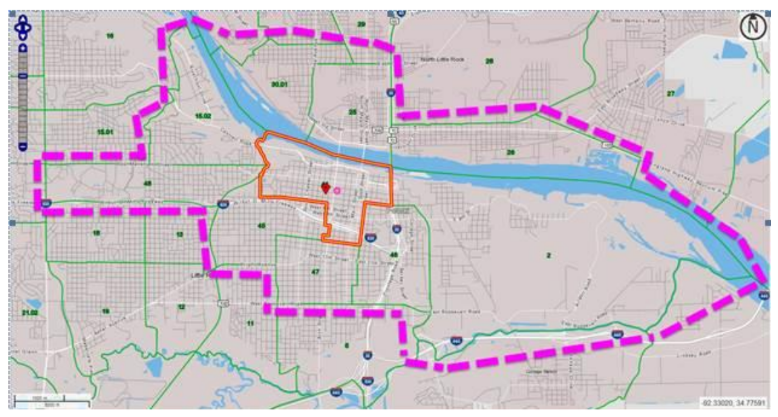
What is a targeted employment area (TEA) and why is it important?
According to the USCIS, the minimum qualifying EB-5 investment is $1.8 million. The minimum qualifying investment within a TEA is $900,000. A TEA is an area that, at the time of investment, is a rural area or an area experiencing unemployment of at least 150 percent of the national average rate. A rural area is any area outside a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) and outside the boundary of any city or town having a population of 20,000 or more according to the decennial census. To see if your location qualifies as a TEA, look HERE.